Personal Health Train
Distributed Privacy-Preserving Data Analysis
Background
In public health research, data sharing is often challenging due to the sensitive nature and heterogeneous characteristics of health data. Moreover, the lack of standardization and semantics further exacerbate the problems of data fragments and data silos, which makes data analytics difficult. While there are great benefits for collaborative analyses across multiple epidemiological studies, data protection concerns and the lack of IT infrastructure currently limit widespread cross-institute research projects. The aim of NFDI4Health is to enable institutes to participate in such
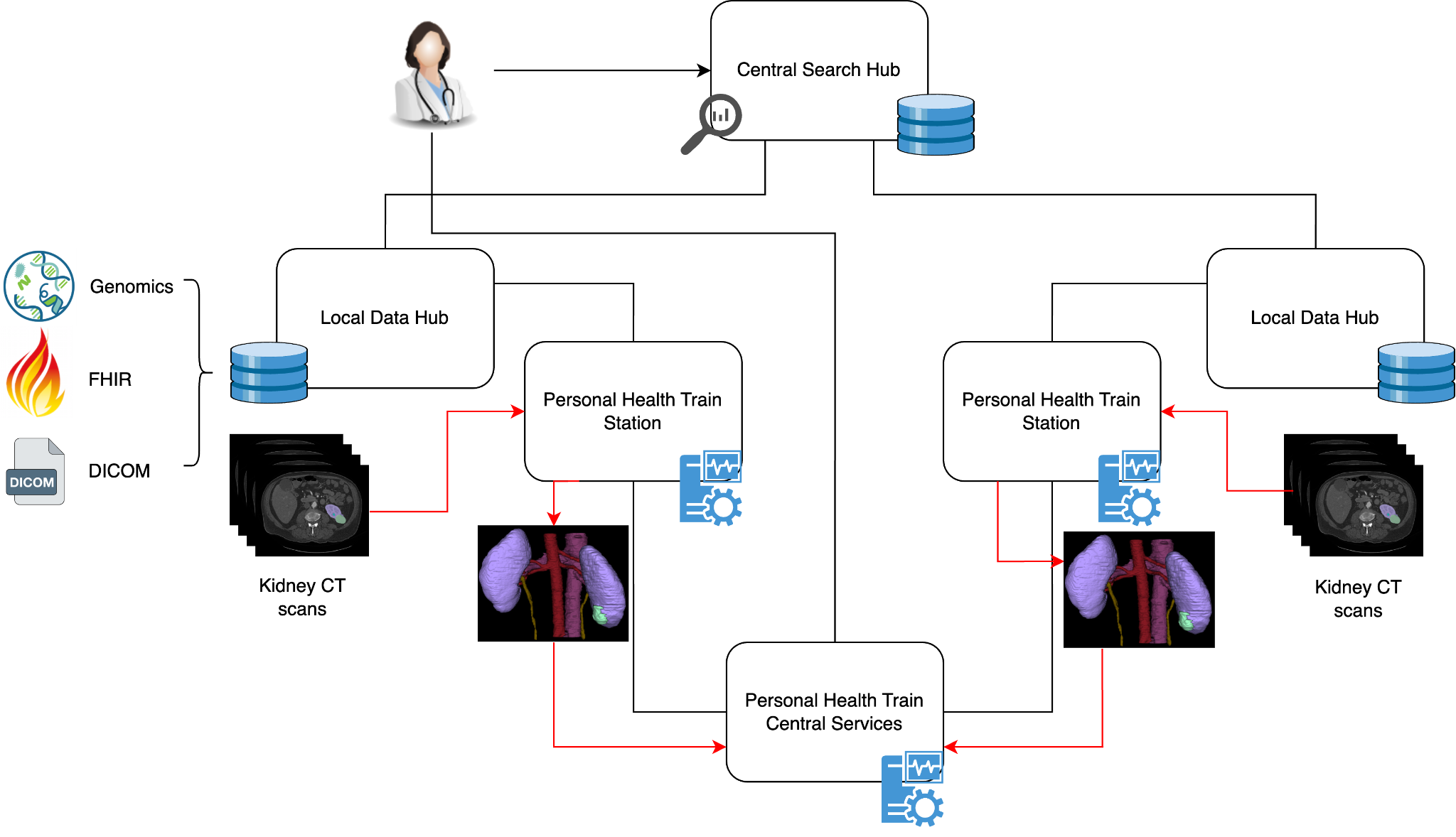
research projects without actually ceding control over their data. One approach to overcome these challenges is federated data analysis with Personal Health Train (PHT). The PHT complements the Central Search Hub (CSH) and Local Data Hub (LDH) by providing the means of executing analysis in a distributed and privacy-preserving manner. Unlike centralized analysis, the PHT brings the algorithm to the data instead of vice versa, enabling data owners to retain control of their data and keeping the data in its origin.
Concept
The Personal Health Train Concept is an innovative approach to foster data-driven innovations in medicine. It provides a distributed analysis infrastructure that enables research on sensitive data without prior data sharing, while supporting diverse data formats. The PHT originates from an analogy from the real world, resembling a railway system with trains, stations, and train depots. In the PHT ecosystem, the train encapsulates an analytical task, represented by the goods in the analogy. The data provider plays the role of a reachable station, accessed by the train. The station executes the task, processing the available data. The Central Service (CS)
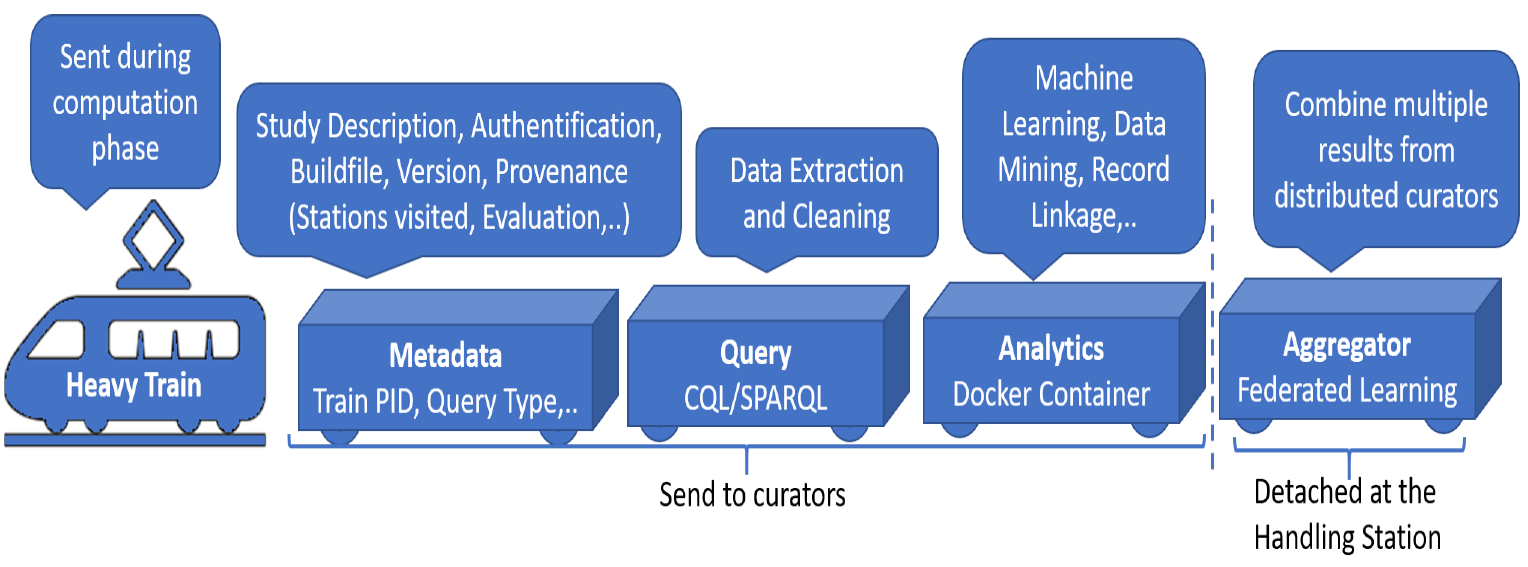
Implementation under NFDI4Health
 English
English  Deutsch
Deutsch 