Activity and Health during the SARS-CoV2 Pandemic (ASAP)

Start date
April 2020
End date
----
Participants
Adults, who are residents of countries affected by COVID-19 and experiencing government restrictions
Main goal
Understanding how people’s physical activity levels and mental health were affected during the COVID-19 pandemic
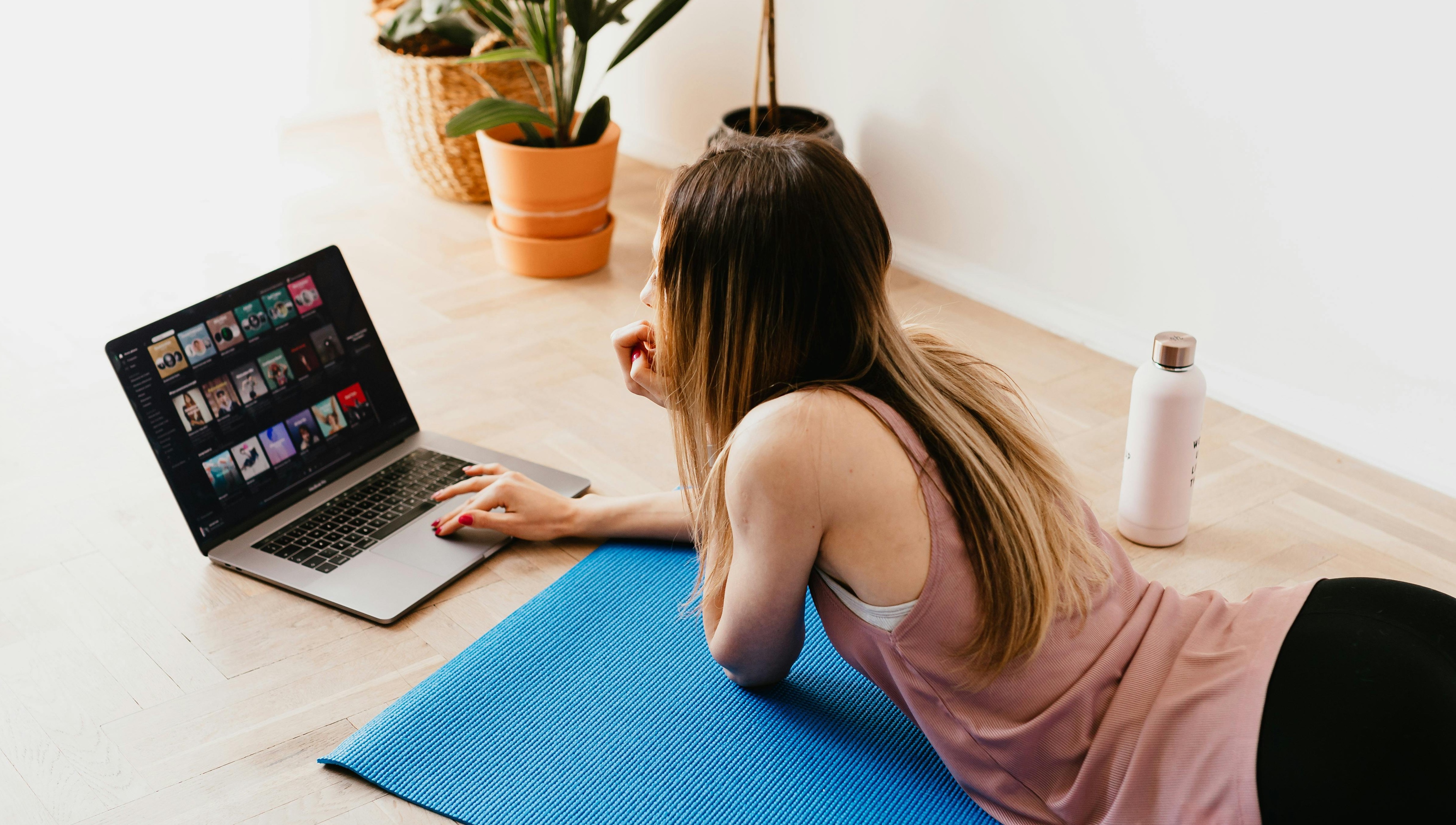
Summary
The ASAP project studied how the COVID-19 pandemic and lockdowns affected people's physical activity and well-being. Researchers wanted to understand if being stuck at home made people less active and how it impacted their mental and physical health. They also tested whether online exercise programs could help people stay active and healthy during these restrictions.
The study was conducted in multiple countries, where participants filled out surveys about their activity levels and health before and during the pandemic. Some participants also took part in online exercise programs. The project aimed to find better ways to support people in staying active during future crises like pandemics. The results could help health officials create better policies to promote active living, even when people can't go outside as much.
Person responsible for the project: Dr. Jan Wilke (wilke@sport.uni-frankfurt.de)
What do we want to achieve?
1
Understanding how physical activity and well-being were affected during the COVID-19 pandemic.
2
Evaluating whether online exercise programs can improve physical activity and health.
3
Collecting data from a diverse group of people about their experiences during lockdowns through surveys.
4
Informing health officials on ways to encourage active living during restrictions.
5
Supporting future research by generating findings on health and physical activity during emergencies.
Results
Decreased physical activity
Lockdowns during the COVID-19 pandemic led to a significant drop in physical activity levels among participants.
Negative Health Effects
Many people reported their physical and mental health got worse because they moved less and spent more time sitting during lockdown.
Interest in Online Exercise
Participants showed a lot of interest in doing exercise programs from home, and they were willing to join online workouts.
Effectiveness of Online Programs
Digital exercise programs were effective in increasing participants' physical activity and improving mental well-being.
Importance of support
Access to structured online exercise programs can provide essential support for maintaining health during periods of social isolation.
Guidance for Future Strategies
The results may inform health policymakers on how to promote physical activity and mental well-being during future public health crises.
Keywords
#physical activity, #coronavirus, #exercise, #isolation, #home-based, #e-health
Further information
Our partners
Johann Wolfgang Goethe-Universität - Department of Sports Medicine, Frankfurt am Main
Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation
Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG)
Progress ASAP


 English
English  Deutsch
Deutsch 